We will contact you shortly to schedule a convenient appointment.
niPGT-A
A state-of-the-art, non-invasive method of examining embryos without interfering with their structures.
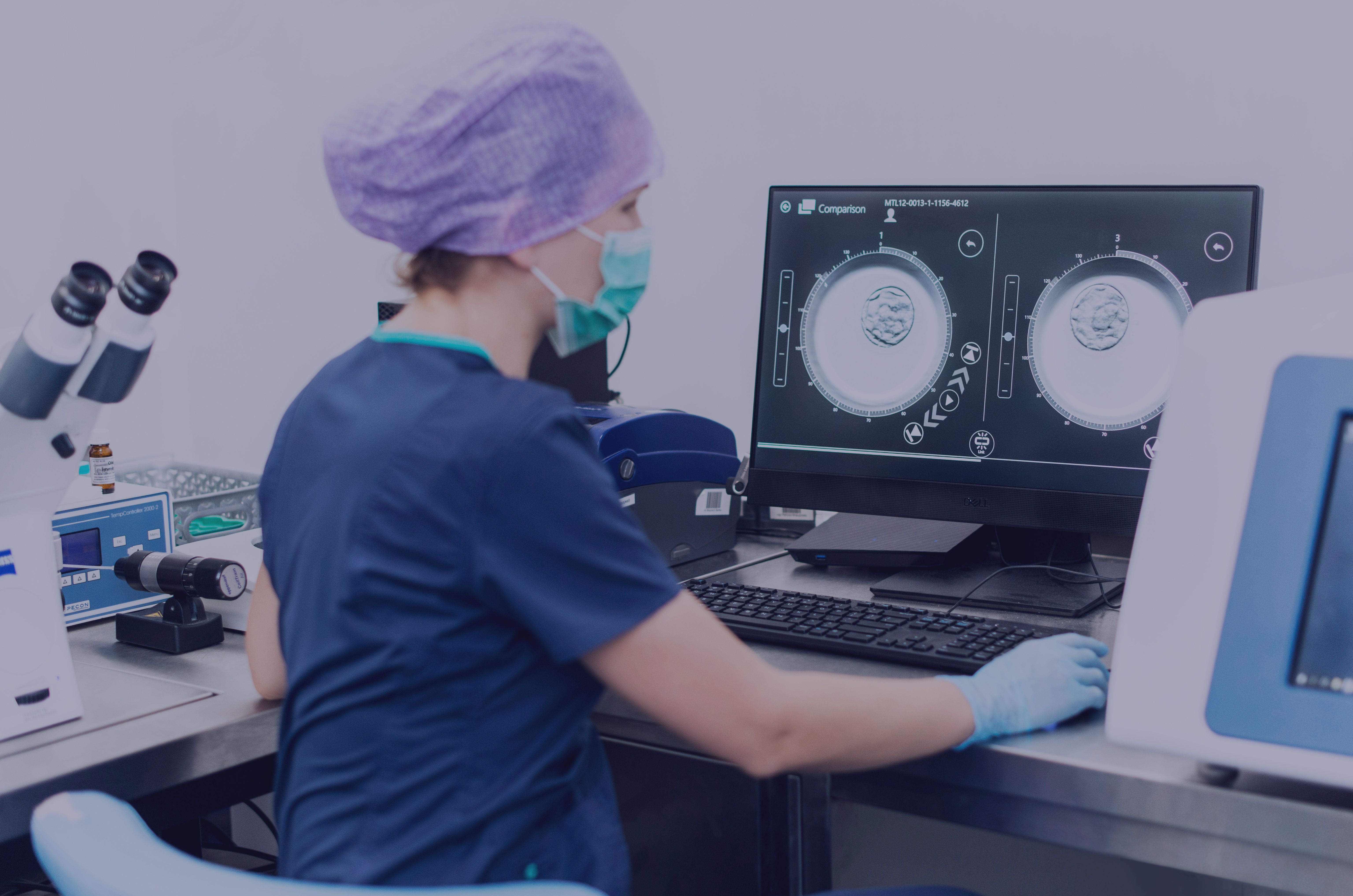
niPGT-A ( non-invasive Preimplantation Genetic Testing for Aneuploidy) is a non-invasive genetic screening test that evaluates the number of all chromosomes present in material taken from the embryo’s culture medium at an early stage of its development, in the first days of the in vitro fertilization procedure. Deviations from the norm in the number of chromosomes are responsible for the majority of miscarriages in the first trimester of pregnancy and the failure of the in vitro procedure.
The niPGT-A test, on the other hand, allows the identification of aneuploidies, i.e. Down syndrome, Patau syndrome, Edwards syndrome, Turner syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome and others, and the selection of a healthy and most promising embryo for transfer.
The Gyncentrum Genetic Laboratory has state-of-the-art human genome sequencing technology for testing embryos from culture fluid. It makes it possible to detect, at a very early stage of embryo development, chromosomal abnormalities with unprecedented accuracy. At the Gyncentrum Genetic Laboratory, in addition to niPGT-A, we also perform other preimplantation genetic tests, including: PGT-A, PGT-M, PGT-SR and Karyomapping.
Are you interested in the niPGT-A genetic test?
Contact us for details
What is the niPGT-A based on?
niPGT-A differs from classical PGT-A in the way the material is collected, which does not interfere with the structures of the embryo. The material to be examined here is only the fluid in which the embryo was cultured, not the trophoectoderm cells. The study showed a correspondence between the DNA of embryonic origin in the culture fluid and the material extracted from the trophoectoderm fragment, as with the traditional PGT-A method.
Make an appointment for a consultationWho should take the niPGT-A test?
A significant number of embryos with aneuploidies, i.e. abnormalities in the number of chromosomes, die already in the first trimester of pregnancy following spontaneous abortion. Sometimes such a pregnancy can be carried to term, but the child is then burdened with a genetic disease, Down syndrome, Edwards syndrome, Patau syndrome or Klinefelter syndrome. niPGT-A is a tool that allows to select embryos with aneuploidies and choose genetically normal ones for transfer. The niPGT-A test is a chance for couples to get pregnant and have a healthy baby:
- approaching the in vitro fertilization procedure,
- experiencing one or more miscarriages,
- after unsuccessful in vitro fertilization procedures,
- in which the partner is older than 35,
- who have been diagnosed as carriers of genetic diseases,
- from families burdened with genetic diseases, in which the disease became clinically apparent,
- after treatment for cancer in the past

What are aneuploidies?
We speak of aneuploidy when the basic set of chromosomes characteristic of a species, or karyotype, is enriched or lacking at least one chromosome. Thus, the cells of such an organism contain a higher or lower number of chromosomes relative to the normal state. Aneuploidies most often arise from the erroneous divergence of chromosomes during cell division (meiosis). Their presence is unfortunately associated with the occurrence of serious birth defects in the child, but most often results in spontaneous miscarriage.
Find out moreExamples of aneuploidy
Trisomy: is the presence of an extra third chromosome in a given homologous pair (in genetics is denoted as 2n+1). In humans, trisomy of chromosome 21 is the cause of Down syndrome, chromosome 18 is the cause of Edwards syndrome, while 13 is the cause of Patau syndrome.
Monosomy: is the absence of one chromosome from a given pair (denoted as 2n-1 in genetics). Monosomy often results in the death of the embryo at an early developmental stage (lethal mutation). In humans, the most common example of monosomy is monosomy of the X chromosome (X0 in the karyotype) responsible for Turner syndrome.



